Maximizing Comfort and Efficiency: Exploring the Benefits of Heat Pumps for Home Heating and Cooling
What are the real gains of installing a heat pump in your home? Beyond the buzzwords, “the benefits of heat pumps for home heating and cooling” are pivotal for achieving low energy consumption, but understanding their true advantages requires a deeper look. This article breaks down the benefits, from tangible cost savings to environmental impact, offering an objective view on why they could be a crucial upgrade for your home comfort system.
Key Takeaways
-
Heat pumps are a versatile and energy-efficient solution for both heating and cooling, providing year-round comfort and resulting in lower energy bills and a reduced carbon footprint.
-
Despite higher initial investment costs, the long-term energy savings, maintenance cost reduction, and available financial incentives make heat pumps a cost-effective choice for homeowners and businesses alike.
-
Innovations in heat pump technology, such as smart thermostats and advanced features for enhanced air quality and comfort, are continually improving the performance and convenience of these systems.
Exploring Heat Pump Advantages

Heat pumps offer a versatile heating and cooling solution, providing year-round comfort with a single system. This dual functionality makes them an attractive option for homeowners looking to optimize their living spaces without compromising on comfort. Not only do heat pumps cater to residential needs, but they also enhance productivity and reduce maintenance costs in commercial environments.
The energy efficiency of heat pumps is another major advantage. By moving heat rather than generating it, they consume significantly less energy compared to traditional heating and cooling systems, such as natural gas or electric resistance heaters. This efficiency translates to lower energy bills, making heat pumps a financially sound investment over time.
Moreover, heat pumps contribute to environmental sustainability. Transitioning to heat pumps can lead to decreased energy expenses and a reduced carbon footprint, demonstrating their combined financial and eco-friendly benefits. These systems are designed to operate efficiently in various climates, further broadening their appeal.
Given these numerous benefits, it’s not surprising that many homeowners are favoring heat pumps. We will now further explore their dual functionality, energy efficiency, and environmentally friendly operation to understand their market prominence.
Dual Functionality: Heating and Cooling in One
One of the standout features of heat pumps is their ability to provide both heating and cooling, effectively serving as a two-in-one system. During the colder months, a heat pump absorbs heat from the outside air and transfers it indoors to warm the home. Conversely, in the summer, it removes heat from the indoor air, providing a cooling effect. This seamless transition between heating and cooling modes ensures year-round comfort without the need for separate systems.
This dual functionality is primarily driven by the reverse cycle mechanism. In heating mode, the heat pump extracts heat from the outdoor air, even in low temperatures, and transfers it inside. In cooling mode, the process is reversed, with the reverse cycle air conditioner removing heat from the indoor air and expelling it outside. This efficient heat exchange process makes heat pumps highly effective in maintaining a comfortable indoor climate.
Split system heat pumps further enhance this functionality with their design. They consist of an outdoor unit that houses the compressor and condenser and an indoor unit with an evaporator coil and fan. This setup allows for efficient heating and cooling of the home, making heat pumps a smart choice for those looking to streamline their climate control solutions.
Energy Efficiency Mastery

Heat pumps are recognized for their superior energy efficiency as they consume considerably less energy than traditional heating and cooling systems. Unlike systems that generate heat, heat pumps move heat from one place to another, which is inherently more efficient. This efficiency is most apparent in reverse cycle air conditioners, a common type of heat pump, which are cheaper to run and generate lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to other heating and cooling appliances.
Selecting high-efficiency models can lead to substantial energy savings. For instance, some models can achieve up to 40% savings compared to standard units. This not only reduces energy consumption but also lowers utility bills, making heat pumps a cost-effective solution in the long run.
The environmental significance of this energy efficiency is immense. By reducing the amount of energy needed to heat or cool a home, heat pumps contribute to a significant decrease in greenhouse gas emissions. This makes them an excellent choice for homeowners looking to reduce their carbon footprint while enjoying the benefits of a modern, efficient heating and cooling system.
Eco-Friendly Operation
As heat pumps run on electricity, potentially generated from renewable sources, they offer an environmentally friendly substitute to traditional systems that rely on fossil fuels. This reliance on electricity helps in curbing greenhouse gas emissions. For example, transitioning from gas furnaces to air-source heat pumps can result in approximately a 40 percent reduction in household carbon dioxide emissions.
For businesses, adopting heat pumps offers several benefits:
-
Significantly diminishing their carbon footprint
-
Enhancing their sustainability image
-
Aligning with corporate responsibility goals
-
Showcasing a commitment to a greener future
This shift not only benefits the environment but also resonates positively with customers who prioritize eco-friendly practices.
The Mechanics of Heat Pumps
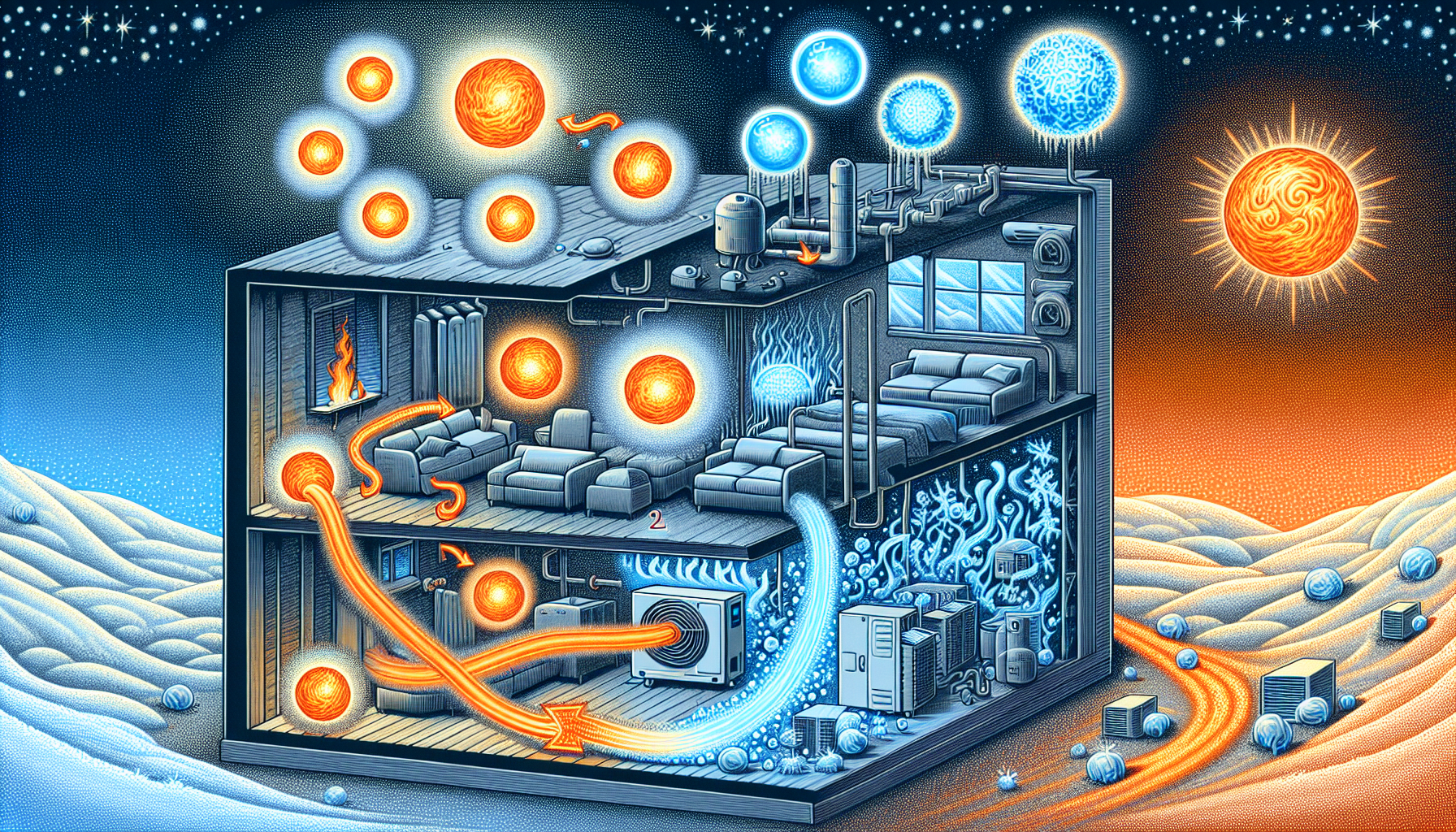
To fully appreciate the efficiency and versatility of heat pumps, it’s important to understand their working mechanism. At the core of their operation is the ability to move heat rather than generate it. This process allows heat pumps to provide an output of up to 10-15 times more energy than they consume. During winter, heat pumps absorb heat from the outside air and transfer it indoors, while in summer, they reverse the process to cool the building.
This transfer heat process is what makes heat pumps so efficient. By utilizing the residual energy present in the air or ground, heat pumps can effectively:
-
Heat or cool a space without the need for additional energy input
-
Enhance comfort
-
Reduce energy consumption
-
Lower utility bills
-
Create a smaller environmental footprint.
A thorough understanding of the mechanics of heat pumps requires examination of the specific processes and components involved. From absorbing heat to transferring it indoors and vice versa, each step plays a crucial role in the overall efficiency and performance of the system. Let’s explore these details further to understand how heat pumps achieve such remarkable results.
The Heat Transfer Process
Heat pumps are designed to absorb warmth from the outdoor air even during cold winter days. This is possible because there is always some residual heat energy present, even at lower temperatures. The heat pump absorbs this warmth and transfers it indoors, providing efficient heating. In contrast, during the summer, the heat pump reverses the process, extracting heat from the indoor air and expelling it outside, thereby cooling the home.
Geothermal heat pumps, which are also known as ground-source heat pumps, operate using a different method. They offer an alternative to traditional heating and cooling systems. They use underground loop systems to transfer natural warmth from the ground to the pump. The ground temperature remains relatively constant throughout the year, making these systems particularly effective in colder climates. This method of heat transfer ensures reliable and efficient heating and cooling, regardless of outdoor conditions.
Heat Pump Components at Work

Advanced components like scroll compressors and variable-speed motors further augment the efficiency of heat pumps. Scroll compressors operate with two spiral-shaped scrolls that compress the refrigerant by forcing it into smaller areas, offering advantages like a longer lifespan and quieter operation compared to piston compressors. These compressors play a critical role in maintaining the system’s efficiency and reliability.
Variable-speed compressors and dual-speed motors are also integral to heat pump efficiency. These components adjust their output to match real-time heating and cooling demand, which not only improves comfort levels but also reduces energy consumption and minimizes noise. Additionally, the use of environmentally friendly refrigerants and advanced heat exchangers further boosts the performance and environmental benefits of heat pumps.
Cost-Effectiveness of Heat Pump Systems
The cost-effectiveness of heat pumps is one of their most attractive features. Despite the higher upfront cost of purchasing and installing a heat pump system, the long-term savings achieved through lower energy bills make them a worthwhile investment. By moving heat rather than generating it, heat pumps consume less energy, leading to substantial savings over time.
Efficient operation of heat pump units essentially depends on their proper sizing. Incorrectly sized units, whether too large or too small, can lead to increased energy bills and higher costs. Regular maintenance also plays a significant role in cost savings. Well-maintained heat pumps can consume 10% to 25% less energy compared to neglected units, further contributing to long-term savings.
Although the initial investment could appear substantial, the long-term advantages of heat pumps, such as energy savings and reduced maintenance costs, typically compensate for the upfront cost. Let’s explore how the upfront investment compares to the long-term savings and the financial incentives available to make this transition more affordable.
Upfront Investment vs. Long-Term Savings
The initial investment in a heat pump system can be significant compared to conventional heating systems. However, homeowners can expect to:
-
Save an average of $459 annually on their energy bills
-
Experience high energy efficiency, resulting in operational cost savings that offset the higher upfront costs over time
-
Take advantage of financial support programs, such as discounted loans through the Household Energy Upgrades Fund, to help lower the upfront investment cost.
These long-term savings and financial aids make heat pumps a financially prudent choice for homeowners looking to reduce their energy expenses and contribute to environmental sustainability.
Incentives and Rebates
Governments are increasingly promoting energy efficiency and eco-friendly alternatives by providing financial incentives for heat pump installations. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront cost of heat pump systems, making them more accessible to homeowners. State and local governments, along with utility companies, offer rebates and tax credits, reflecting growing support for heat pumps.
Additional incentives may be available for specific residential heating upgrades, such as replacing fireplaces with electric or gas heating systems. These financial aids not only make the transition to heat pumps more affordable but also encourage broader adoption of this efficient and eco-friendly technology.
Adapting to Climate Variations
Heat pumps offer remarkable adaptability, efficiently operating under diverse climates. Cold climate heat pumps, including air source heat pumps, are specially designed to perform well even in regions with lower temperatures, eliminating the need for supplementary heating systems. This makes them a viable option for areas that experience harsh winters, ensuring consistent heating without significantly increasing energy consumption.
The Department of Energy has recognized the potential of heat pumps in colder climates and has launched the Residential Cold Climate Heat Pump Technology Challenge. This initiative aims to stimulate the advancement and wider deployment of high-performing cold climate heat pump technologies. However, it’s important to note that heat pump efficiency begins to decrease at around 40 degrees Fahrenheit, which can pose challenges during extreme cold weather.
The decision between geothermal and air source heat pumps necessitates thoughtful evaluation of available space and particular climate conditions. This decision can significantly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of the heating and cooling system, making it crucial to understand the suitability of different heat pumps for various climates.
Suitability Across Various Climates
Geothermal heating systems are particularly efficient in colder climates, thanks to their ability to utilize the constant temperature of the ground. These systems use a ground loop system comprising water pipes to absorb heat from the ground before it is compressed and transferred into the home heating system. This makes them an excellent choice for regions with severe winters, where maintaining a consistent indoor temperature is essential.
On the other hand, air source heat pumps, a type of air source heat pump, are better suited for milder climates. They extract heat from the outdoor air, making them ideal for areas where the temperature does not drop drastically. Understanding these distinctions helps homeowners choose the most suitable heat pump for their specific climate conditions, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Enhancements for Extreme Weather

Hybrid systems, which integrate a heat pump with a gas furnace, offer a practical solution for improving heat pump efficiency in extreme weather conditions. These systems switch between the heat pump and the furnace depending on the temperature, ensuring efficient heating even at low temperatures. Additionally, the combination of heat pumps with solar power can provide hot water and heating in various weather conditions, further enhancing their versatility.
Modern heat pumps are equipped with advanced defrosting mechanisms to maintain consistent heating performance by minimizing frost buildup in colder climates. Split heat pump systems, with their detached components and larger heat exchangers, are also more adept at handling extreme weather conditions. These enhancements ensure that heat pumps remain reliable and efficient, regardless of outdoor temperatures.
Maintenance and Longevity of Heat Pumps
Minimal maintenance requirements are among the numerous advantages of heat pumps. With just a routine system check once a year and regular cleaning or replacing of filters, homeowners can ensure their heat pump operates efficiently. This simplicity in maintenance not only saves time but also reduces the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs.
Regular maintenance tasks for outdoor coils and heat pumps include:
-
Cleaning the outdoor coils to ensure they are free from dust and debris
-
Checking for any minor problems and addressing them before they escalate
-
Adhering to a maintenance checklist to ensure all necessary tasks are completed
-
Conducting routine checks to maintain optimal function and prevent potential issues
By regularly performing these maintenance tasks, you can prevent issues and maintain the heat transfer efficiency of your heat pump, ultimately extending its overall lifespan.
By adhering to these straightforward maintenance routines, homeowners can reap the benefits of a well-performing heat pump over an extended period. Let’s delve deeper into these maintenance tasks and discuss the expected lifespan and warranty coverage for heat pumps.
Simple Maintenance Routines
Regular maintenance for heat pumps includes essential tasks such as checking thermostats, replacing or cleaning air filters, and examining blower belts and motors. Keeping smart thermostats properly maintained is also crucial, which involves cleaning sensors and troubleshooting connectivity issues. These tasks ensure that the heat pump operates efficiently and effectively throughout its lifespan.
Seasonal maintenance is particularly important. This involves replacing air filters and clearing any snow or debris from the outdoor unit, especially during winter. Additionally, an annual professional maintenance check-up is recommended to sustain the heat pump’s performance and address any potential issues early on.
Life Expectancy and Warranty Coverage
Heat pumps have a long lifespan, with some models capable of lasting up to 50 years. Although specific warranty details vary by manufacturer, homeowners can generally expect their heat pump systems to be backed by a warranty that protects their investment and offers peace of mind.
This combination of longevity and reliable warranty coverage makes heat pumps a durable and secure choice for home heating and cooling.
Tailoring Your Heat Pump to Your Home
Selecting an appropriate heat pump entails taking into account various factors such as climate, home size, and compatibility with existing systems. Proper selection ensures that the heat pump meets the home’s heating and cooling needs effectively. This process begins with assessing the home’s thermal performance, including insulation levels and the number of windows, which affect heat loss and gain.
Ensuring existing ductwork is free from leaks, gaps, or insulation problems is also crucial for the optimal performance of a new heat pump. By addressing these factors, homeowners can maximize the efficiency and comfort provided by their heat pump system. Let’s explore how to select the correct size and integrate the heat pump with existing systems.
Selecting the Correct Size
Proper sizing of a heat pump is essential to prevent unnecessary energy use and maintain efficient and comfortable heating and cooling. The Manual J calculation method is highly recommended for selecting the correct heat pump size, as it takes into account local climate conditions, the layout of the house, and insulation quality. This meticulous approach ensures that the heat pump is neither too large nor too small, both of which can lead to inefficiencies and higher energy costs.
A rough sizing guide indicates that each 500 square feet of a home typically necessitates one ton of heat pump capacity. By following these guidelines, homeowners can ensure that their heat pump is appropriately sized, leading to optimal performance and energy savings.
Integration with Existing Systems
Geothermal systems are generally easier to integrate into new constructions, while air source heat pumps are more suitable for installation in existing homes. Hybrid systems enable the combination of heat pumps with existing heating systems, optimally switching between them depending on the temperature through integrated controls. This flexibility ensures that the home remains comfortable regardless of the weather outside.
Creating heating zones with a heat pump facilitates efficient and tailored heating and cooling of specific home areas, leading to enhanced comfort and reduced energy use in unoccupied spaces. Some benefits of creating heating zones with a heat pump include:
-
Adding heating or cooling to parts of a home that are not covered by the central system, such as new additions or areas with no existing ductwork
-
Flexibility in controlling the temperature of different areas of the home
-
Energy savings by only heating or cooling occupied areas
-
Increased comfort by customizing the temperature in different zones
These integration options make heat pumps a versatile choice for various home setups.
Innovative Heat Pump Technologies
The comfort and efficiency of these systems, including air conditioning, is constantly being improved by innovative heat pump technologies. Smart thermostat technology, for instance, allows for enhanced climate control, enabling homeowners to remotely manage their heating and cooling settings. This intelligent temperature management adapts to user lifestyles, ensuring optimal comfort and energy efficiency.
The overall performance enhancements of heat pumps are significantly influenced by advanced features and energy management systems. These technologies not only improve the efficiency of heat pumps but also provide additional benefits such as improved indoor air quality and predictive maintenance alerts. Let’s explore these innovations in more detail.
Smart Controls and Connectivity
Smart thermostats for heat pumps offer a range of advanced features, including remote control capabilities, scheduling, and energy usage monitoring. These features integrate seamlessly with other smart home devices, enhancing overall energy efficiency. Intelligent controls allow for remote monitoring and adjustment of heat pump settings, optimizing energy use and providing user convenience.
Emerging technologies in smart thermostats may soon include capabilities to monitor indoor air quality and predict maintenance needs, further enhancing comfort and efficiency. The compatibility of smart thermostats with various heat pump models facilitates easy integration into existing home infrastructures without major modifications.
Advanced Features for Enhanced Comfort
Heat pumps improve indoor air quality by filtering the air and dehumidifying the environment, which enhances overall comfort levels. These advanced features ensure that the indoor environment remains healthy and comfortable, making heat pumps an attractive option for homeowners seeking to improve their living conditions by introducing warm air.
Additionally, the ability to control and monitor these features remotely allows for a more personalized and efficient heating and cooling experience. This not only improves comfort but also contributes to significant energy savings. Some benefits of heat pumps include:
-
More personalized and efficient heating and cooling experience
-
Remote control and monitoring capabilities
-
Significant energy savings
-
Smart and sustainable choice for modern homes
Summary
In summary, heat pumps offer a versatile, energy-efficient, and eco-friendly solution for home heating and cooling. Their dual functionality, combined with advanced technologies and minimal maintenance requirements, make them an attractive option for homeowners looking to optimize their living spaces. The long-term cost savings and environmental benefits further enhance their appeal, making heat pumps a smart investment for the future.
As we continue to seek sustainable and efficient ways to manage our home environments, heat pumps stand out as a leading solution. Their ability to adapt to various climates, coupled with innovative features that enhance comfort and efficiency, ensures that they will remain a valuable asset for years to come. Consider adopting a heat pump system to enjoy the benefits of modern, efficient, and eco-friendly home heating and cooling.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main benefits of using a heat pump?
The main benefits of using a heat pump include dual functionality for heating and cooling, high energy efficiency leading to lower utility bills, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and eco-friendly operation on electricity instead of fossil fuels.
How do heat pumps work in cold climates?
In cold climates, heat pumps work efficiently by absorbing heat from the outdoor air and transferring it indoors for heating, while geothermal heat pumps use underground loop systems to maintain efficiency.
What maintenance is required for a heat pump?
To maintain a heat pump, you should schedule routine system checks, clean or replace filters regularly, and keep outdoor coils free from dust and debris. It is also recommended to have a professional check-up once a year.
Are there any financial incentives for installing a heat pump?
Yes, governments and utility companies offer rebates and tax credits for heat pump installations, which can lower the upfront cost and make them more accessible to homeowners.
How do I choose the right size heat pump for my home?
To choose the right size heat pump for your home, it's crucial to use the Manual J calculation method, considering factors like local climate, house layout, and insulation. As a rough guide, aim for one ton of heat pump capacity per 500 square feet of your home.








